Tutorial 4b – FE-plate problem
In this tutorial we use Fesslix to analyze a finite element plate (using finite elements with linear shape functions).
Table of Contents
1 Mechanical model
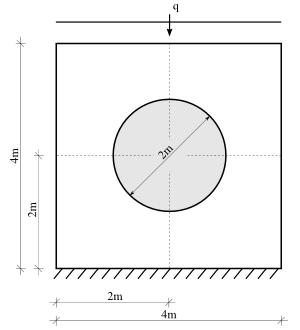
We investigate the problem of the following linear elastic finite element plate with a hole:
where the distributed load q is 5kN/m. The Young's modulus of the plate is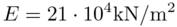 , and
the thickness of the plate is 0.1m.
, and
the thickness of the plate is 0.1m.
where the distributed load q is 5kN/m. The Young's modulus of the plate is
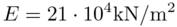 , and
the thickness of the plate is 0.1m.
, and
the thickness of the plate is 0.1m.
2 Step by Step Instruction
Fesslix parameter file
#! ===============================
#! Load the FE module
#! ===============================
loadlib "fem";
#! ===============================
#! Load the FE mesh
#! ===============================
# The mesh is imported from a file.
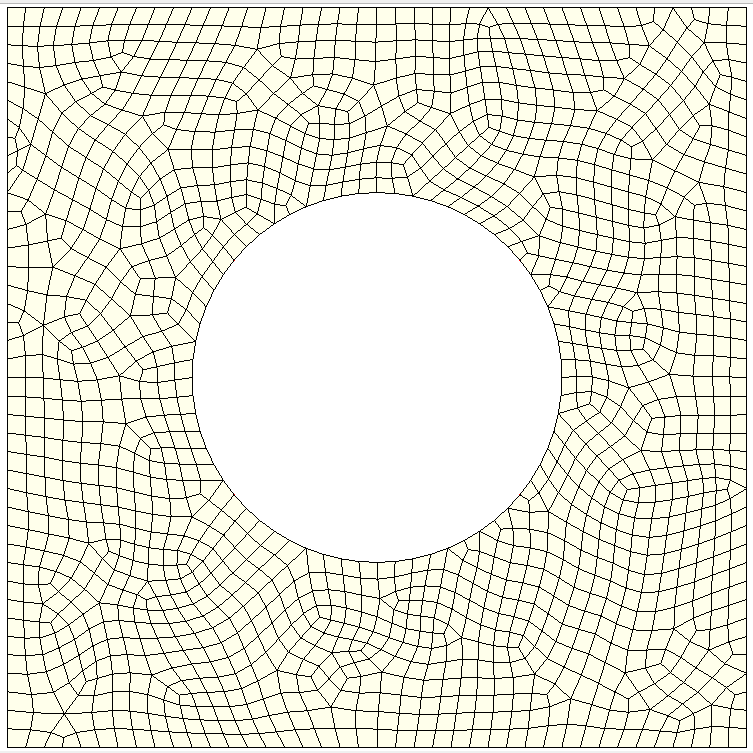
# Different input meshes with varying resolutions are available in the sub-folder 'meshes'.
#! –––––––––––––––-
#! preliminary definitions
#! –––––––––––––––-
# Material that has Young's modulus E
isomat 0 E 21e4 nu 0;
# Load case with a multiplier of 5
loadcase 0 { factor = 5; };
# The mesh to import specifies q as 1.
# Thus, we should view the multiplier as the distributed load q; i.e., 5kN/m.
#! –––––––––––––––-
#! import the mesh
#! –––––––––––––––-
# Define constant that specifies the mesh resolution
const MESH = 2; # integer between 1 and 10 (larger integer result in a finer mesh)
# Import the mesh
# we import the file "meshes/plate_hole_2.dat", where the file-format is 'ps2Ddomesh'.
data_import("meshes/plate_hole_" & {MESH} & ".dat",ps2Ddomesh) {
material = 0; # the material-number to assign to the elements of the mesh
t = 0.1; # the thickness of the plate elements
planestress = true;
loadcase = 0; # the number of the load-case to utilize
};
# Using the format 'SOFiSTiK', we could alternatively import a SOFiSTiK mesh.
#! ===============================
#! Solve the FE-system
#! ===============================
fem assdof; # assemble degrees of freedom
fem assstf; # assemble stiffness matrix
fem assforces; # assemble forces
fem solve; # solve the system
#! ===============================
#! Post-processing
#! ===============================
# Output the vertical (wy) and horizontal (wx) displacement
# at the left (node 4) and right (node 3) upper corner of the plate:
funplot nodeu([4,wy]), nodeu([3,wy]), nodeu([4,wx]), nodeu([3,wx]);
#! Load the FE module
#! ===============================
loadlib "fem";
#! ===============================
#! Load the FE mesh
#! ===============================
# The mesh is imported from a file.
# Different input meshes with varying resolutions are available in the sub-folder 'meshes'.
#! –––––––––––––––-
#! preliminary definitions
#! –––––––––––––––-
# Material that has Young's modulus E
isomat 0 E 21e4 nu 0;
# Load case with a multiplier of 5
loadcase 0 { factor = 5; };
# The mesh to import specifies q as 1.
# Thus, we should view the multiplier as the distributed load q; i.e., 5kN/m.
#! –––––––––––––––-
#! import the mesh
#! –––––––––––––––-
# Define constant that specifies the mesh resolution
const MESH = 2; # integer between 1 and 10 (larger integer result in a finer mesh)
# Import the mesh
# we import the file "meshes/plate_hole_2.dat", where the file-format is 'ps2Ddomesh'.
data_import("meshes/plate_hole_" & {MESH} & ".dat",ps2Ddomesh) {
material = 0; # the material-number to assign to the elements of the mesh
t = 0.1; # the thickness of the plate elements
planestress = true;
loadcase = 0; # the number of the load-case to utilize
};
# Using the format 'SOFiSTiK', we could alternatively import a SOFiSTiK mesh.
#! ===============================
#! Solve the FE-system
#! ===============================
fem assdof; # assemble degrees of freedom
fem assstf; # assemble stiffness matrix
fem assforces; # assemble forces
fem solve; # solve the system
#! ===============================
#! Post-processing
#! ===============================
# Output the vertical (wy) and horizontal (wx) displacement
# at the left (node 4) and right (node 3) upper corner of the plate:
funplot nodeu([4,wy]), nodeu([3,wy]), nodeu([4,wx]), nodeu([3,wx]);
This should return a displacement of 1.16mm in vertical direction and 0.35mm in horizontal direction.